Using Testkube with ArgoCD
This document describes how you can use Testkube with ArgoCD. As a prerequisite, you should have good understanding of both Testkube, ArgoCD and GitOps principles.
For a high-level introduction to using Testkube with ArgoCD including a step-by-step tutorial, please check out our GitOps blogpost and watch our YouTube video:
Managing Testkube CRDs with ArgoCD
Testkube stores its core resources (Workflows, Triggers, etc.) as Custom Resources in your Kubernetes Cluster - Read More about Testkube CRDs. This makes it straightforward to manage them using a GitOps approach with a tool like ArgoCD.
To use Testkube Resources in the synced cluster, the target namespace will need to have the Testkube Agent installed (since the Agent can currently only work with Testkube Resources in its own namespace).
If the Testkube Agent is connected to an Environment in the Testkube Control Plane (either on-prem or in Testkube Cloud), you will see corresponding Testkube Resources in the Testkube Dashboard as soon as they are synced into your cluster by ArgoCD, and be able to trigger/manage them.
In line with GitOps principles, any changes that you make to Testkube Resources in your cluster via the Testkube CLI or Dashboard will be overwritten by ArgoCD when it syncs these resources against your Git repo (since the Git repo is the source of truth for the state of your cluster). Therefore, make sure to make desired modifications to your Testkube Resources in your Git repo instead.
Avoiding pruning of intermediate Testkube Resources
When running your Workflows, Testkube generates intermediate Job and Pod resources as described in Workflows Architecture. If ArgoCD is performing a sync with pruning enabled while Testkube is executing Workflows, there is a high likelihood that these intermediate resources will be deleted by Argo, resulting in aborted/distrupted Workflow executions.
To avoid this you will need to add the below annotations to the generated Job and Pod resources as described in Test Workflows - Job and Pod.
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/compare-options: IgnoreExtraneous
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-options: Prune=false
You can create a Workflow Template that adds these annotations to all your Workflows, instead of adding them manually.
Using the Testkube Agent with ArgoCD
Since the Testkube Agent needs to be installed in the target namespace for your Argo Application(s), you will need to either
- Preinstall the Agent in the target namespace and disable pruning in ArgoCD.
- Include the Testkube Agent manifests or Helm Chart in your ArgoCD Application.
Pre-install the Agent and disable Pruning
This option is more suited for long-lived namespaces - for example a dedicated namespace for a staging or development environment.
When pre-installing the Testkube Agent in your target namespace, it is important to NOT select the prune option when auto-syncing your
Application with Argo, otherwise Argo will remove the Agent from your namespace when syncing.
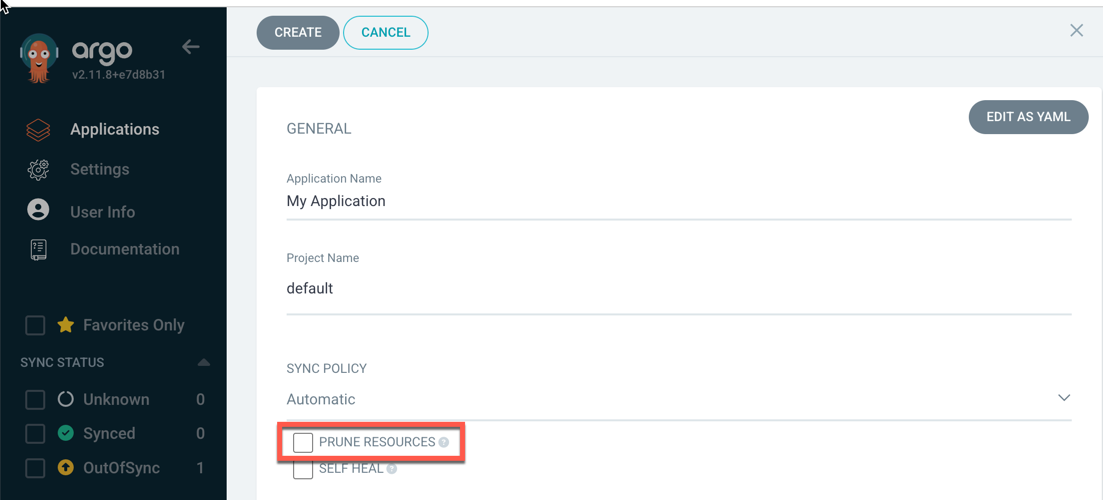
Same applies to manual synchronization - do NOT select the prune option:
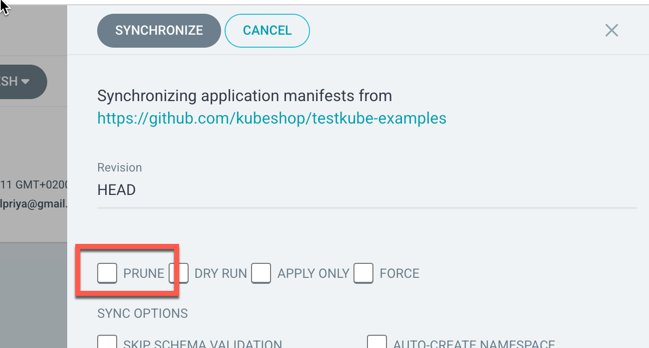
Include the Agent in your GitOps Repo
For ephemeral namespaces it can be more convenient to include the Agent manifests in your GitOps repo so the Agent
gets installed and synced together with any other resources you are managing with ArgoCD. You can simply use helm template
with the Testkube Helm Chart to generate the manifests to be added to your repository.
Alternatively you can make use of the Multiple Source for an Application feature of ArgoCD, including the Testkube Helm chart as an external source:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
spec:
sources:
- repoURL: 'https://kubeshop.github.io/helm-charts'
chart: testkube
targetRevision: 2.1.22
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/charts/testkube-agent/values.yaml
- repoURL: 'https://git.example.com/org/test-repository.git'
targetRevision: dev
ref: values
This example installs the Testkube Agent Helm Chart version 2.1.22 together with Kubernetes resources defined in the
https://git.example.com/org/test-repository.git repository. A values file at /charts/testkube-agent/values.yaml
in this repository is used to configure the Helm installation of the Agent.
Connecting the Agent to a Control Plane
If you want to connect the Agent to a Testkube Control Plane (for storing results, troubleshooting, etc), your values file will require at least the following properties:
testkube-api:
cloud:
key: tkcagnt_XXX
orgId: tkcorg_ZZZ
envId: tkcenv_YYY
url: <url>
minio:
enabled: false
mongodb:
enabled: false
testkube-dashboard:
enabled: false
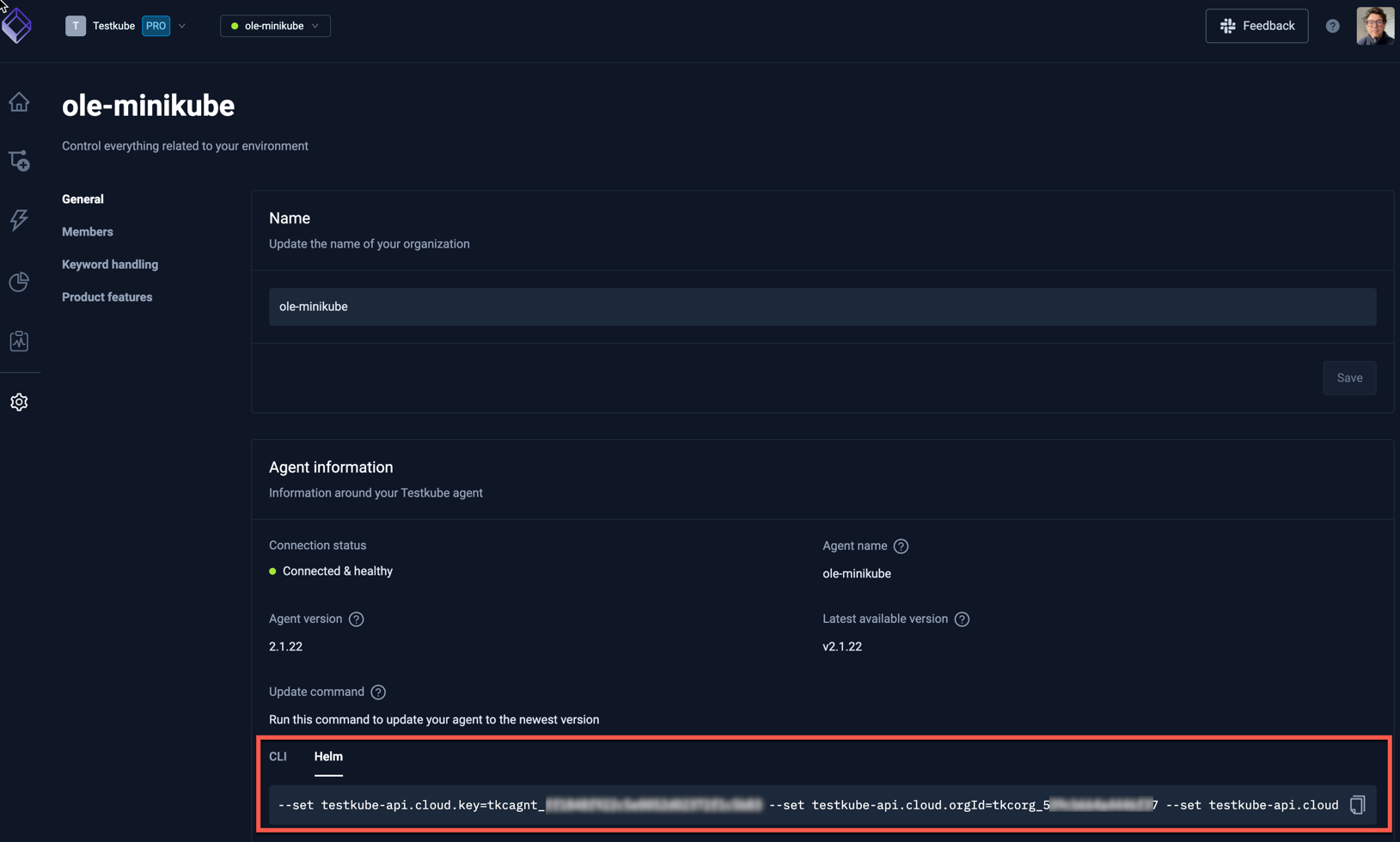
You can find the corresponding values in the Environment Settings for the Testkube Environment that the Agent should connect to:
Triggering Test Executions
Once any Testkube Test Workflows have been synced to your cluster(s) it is likely that you will want to trigger these to execute corresponding Tests. You can of course trigger them manually through the CLI or Dashboard, it will probably make more sense to trigger them either using an ArgoCD Resource Hook or a Testkube Kubernetes Trigger.
- Using a Kubernetes Trigger has the advantage of being disconnected from ArgoCD; whenever a resource gets updated in your cluster, be it by ArgoCD or
some other process (
kubectl, etc.), your tests will always execute. The downside is that they will execute even if your resources are part of a larger application, which might fail synchronizing or not be initialized correctly when the test is triggered. - Using an ArgoCD Resource Hook handles the downside of Kubernetes Triggers by being more attune to the overall ArgoCD sync status; if ArgoCD for some reason fails to sync your application resources with your cluster, it won't run your tests unnecessarily (unless you want it to).
Let's have a quick look on how to set up these two approaches.
Trigger from an ArgoCD Resource Hook
Post-sync Resource hooks are executed by Argo after it has successfully synced resources within an Application - Read More.
Creating a Post-sync hook as a Kubernetes Job that runs Testkube Tests using the Testkube CLI is straightforward; the Job would be defined together with your Testkube Resource in your Git repo and ArgoCD will execute it if the synchronization of Git Resources to your Cluster is successful.
The general outline of such a Post-Sync Job is as follows:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: testkube-testworkflows-execution-
namespace: default
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PostSync
argocd.argoproj.io/hook-delete-policy: HookSucceeded
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: execute-testworkflows
image: kubeshop/testkube-cli:2.1.19
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- |
testkube set context \
--api-key tkcapi_ZZZZ \
--root-domain testkube.io \
--org-id tkcorg_XXXX \
--env-id tkcenv_YYYY
testkube run tw <name-of-workflow> -f
restartPolicy: Never
The Job first sets the Testkube CLI context and then simply invokes the testkube run command for each Workflow that was synced, with the -f option to capture the output.
(here you can obviously run any combination of Testkube CLI commands).
- The
tkcorg_XXXXandtkcenv_YYYYidentifiers can be found on the Environment Settings page. - The
tkcapi_ZZZZapi-key needs to created as described under API Token Management. - the
root-domainshould betestkube.ioif you're using Testkube Cloud, or your local Testkube API endpoint for on-prem installations.
This blog-post contains a complete example of a Post-Sync Resource Hook with video and screenshots.
Trigger using a Kubernetes Event Trigger
Defining a Kubernetes Trigger to react to resources being updated by ArgoCD is equally straightforward. See Kubernetes Triggers for a walkthrough of the Testkube Triggering functionality, let's just look at a short example below:
apiVersion: tests.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestTrigger
metadata:
name: testtrigger-example
namespace: default
spec:
resource: deployment
resourceSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
testkube.io/tier: backend
event: modified
conditionSpec:
timeout: 100
delay: 2
conditions:
- type: Progressing
status: "True"
reason: "NewReplicaSetAvailable"
ttl: 60
- type: Available
status: "True"
action: run
execution: workflow
concurrencyPolicy: allow
testSelector:
name: frontend-sanity-tests
This will trigger the execution of the "frontend-sanity-tests" Test Workflow when any Kubernetes deployment with the
label testkube.io/tier: backend has been modified in the default namespace, which includes updates performed by ArgoCD
during resource synchronization.
Since Triggers are dependent on the target Workflows they execute, be sure to assign them an ArgoCD Sync Wave accordingly; you probably want them to be synced after their target Workflows are synced, but before the actual resources they trigger on are available.